
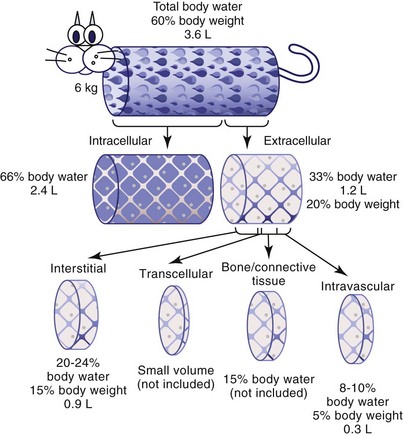
The balance consists of cerebrospinal fluid, lymph, the synovial fluid in the joints, pleural fluid in the pleural cavities (lungs), pericardial fluid around the heart, peritoneal fluid in the peritoneal cavity ( abdomen), and the aqueous humor of the eye. Plasma is the only major fluid compartment that. The two main components of ECF are plasma and interstitial fluid (IF). Interstitial fluid (ISF) consists of all the bits of fluid which lie in the interstices of all body tissues. Osmotic pressure gradients between compartments controls the exchange of solutes and fluids.ECFs are any body fluids that are not inside cells. Intravasular protein > interstitial proteinĪlbumin is the primary intravascular protein - large molecule protein that is not able to diffuse out of the blood vessel under normal circumstances. The remainder is within the extracellular space as the Extracellular Fluid (. Major solutes in intravascular and interstitial fluids: Two-thirds of total body water is held within cells as Intracellular Fluid (ICF). Interstitial space – the loose space between cells, lymphatics, connective tissue, bone Major intracellular solutes (electrolytes)Įxtracellular (ECF): approximately 1/3rd of body's water located is spaces outside of the cells. Total body water can be subdivided into two major compartments, intracellular fluid which is fluid inside cells, and extracellular fluid which is fluid outside of cell like in the blood and in the interstitial tissue between cells.
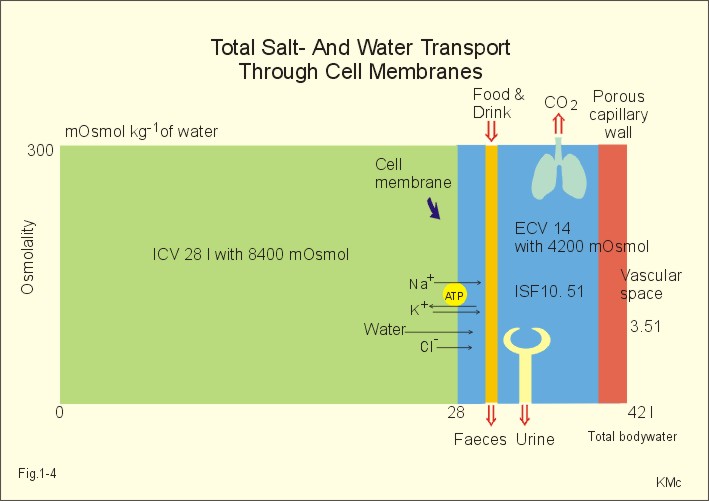
Intracellular (ICF): approximately 2/3rds of body's water located within the cells of the body Men > Women due to larger proportion of muscle massĭistributed in the following two major fluid compartments in the body:

Percentage depends on weight, gender, and age Figure 26.1.2 Fluid Compartments in the Human Body: The intracellular fluid (ICF) is the fluid within cells.
Major body fluid compartments update#
To update your cookie settings, please visit the Cookie Preference Center for this site. For clinical purposes, total body water (TBW) is distributed into two compartments: the intracellular fluid (ICF) compartment (2/3 of TBW) and the extracellular. We can compute the concentration of any solution using the following equation: mEq/L ion concentration (mg/L) divided by the. We use cookies to help provide and enhance our service and tailor content. Electrolyte concentrations of body fluids are usually expressed in milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L), a measure of the number of electrical charges in one liter of solution.

We are aqueous beings! 45-80% of body weight is due to water. The major fluid compartments of the body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
